
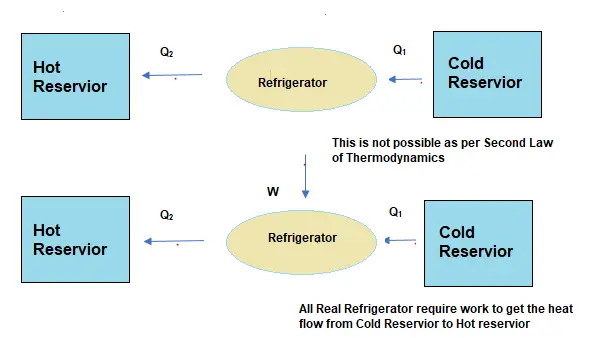
It follows, perpetual motion machines of the second kind are impossible. From this law follows that it is impossible to construct a device that operates on a cycle and whose sole effect is the transfer of heat from a cooler body to a hotter body. Reversible processes are a useful and convenient theoretical fiction, but do not occur in nature. This law indicates the irreversibility of natural processes.
In a natural thermodynamic process, the sum of the entropies of the interacting thermodynamic systems increases. The entropy of any isolated system never decreases. It follows, perpetual motion machines of the first kind are impossible. It is the most important law for analysis of most systems and the one that quantifies how thermal energy is transformed to other forms of energy. This law is the principle of conservation of energy. The increase in internal energy of a closed system is equal to the heat supplied to the system minus work done by it.

This law provides a definition and method of defining temperatures, perhaps the most important intensive property of a system when dealing with thermal energy conversion problems. If two systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.

These are considered as one of the most important laws in all of physics. There are four laws of thermodynamics that define fundamental physical quantities (temperature, energy, and entropy) and that characterize thermodynamic systems at thermal equilibrium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
